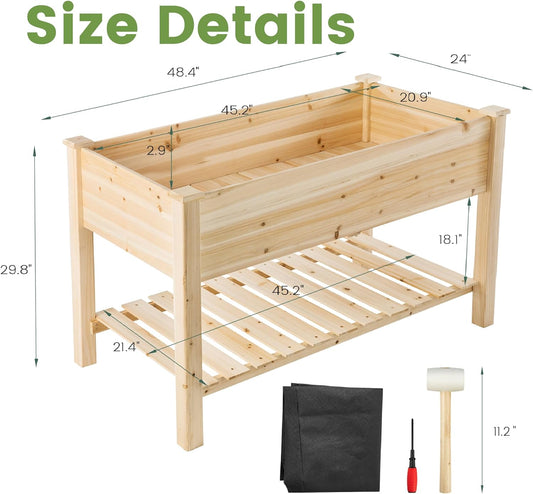
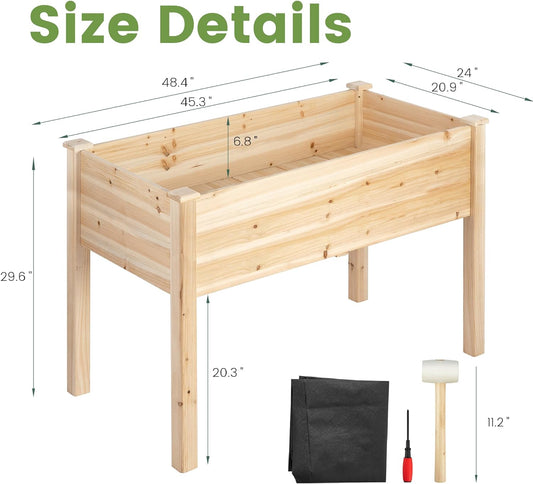
Gargen Bed
Craft your dream garden, one plant at a time.
-
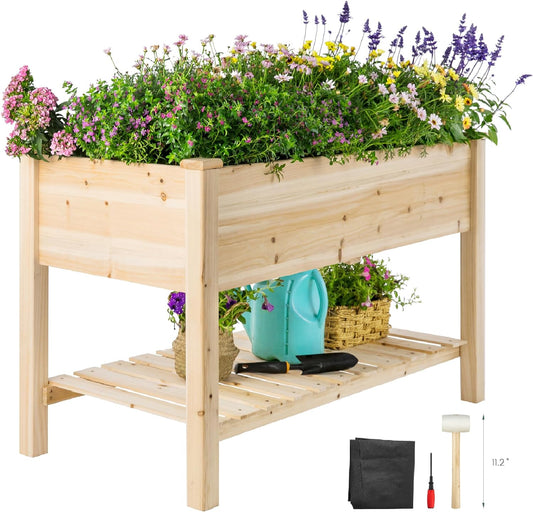
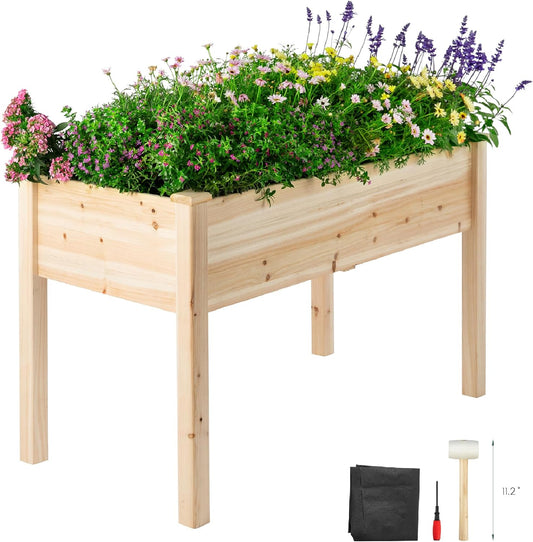
Breltam Outdoor Wood Tall Raised Garden Beds with Legs and Large Storage Shelf for Flower and Vego, Elevated Planter Box Stand for Backyard
Regular price From $79.99Regular priceUnit price / per$149.99Sale price From $79.99Sold out -
Breltam Outdoor Standing Raised Planter Boxes on Legs for Gardening
Regular price $69.99Regular priceUnit price / per$169.99Sale price $69.99Sold out -
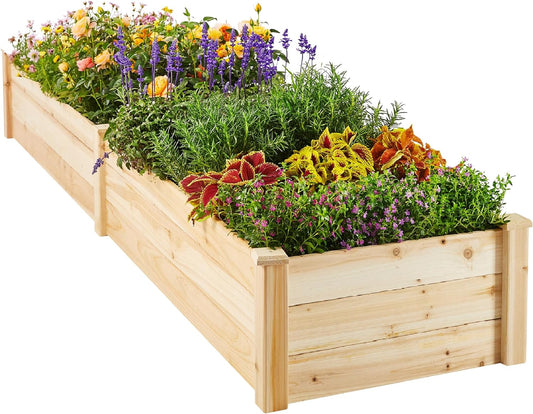

 Sold out
Sold outBreltam Lowes Planter Box
Regular price $69.99Regular priceUnit price / per$129.99Sale price $69.99Sold out
FAQ
What materials are commonly used to construct garden beds?
Garden beds are typically constructed using a variety of materials such as wood, metal, plastic, and composite materials. Wood, particularly cedar and redwood, is popular due to its natural aesthetic and durability. Metal options include galvanized steel or aluminum, known for their longevity and resistance to corrosion. Plastic and composite materials offer lightweight and low-maintenance alternatives.
How deep should a garden bed be for optimal plant growth?
The ideal depth of a garden bed depends on the types of plants you intend to grow. Generally, a depth of 6 to 12 inches is suitable for most vegetables, herbs, and flowers. However, for root vegetables like carrots or potatoes, deeper beds of 12 to 18 inches may be necessary to accommodate their growth.
Do garden beds require any special maintenance?
Garden beds typically require minimal maintenance compared to traditional gardens. Regular watering, weeding, and occasional fertilization are necessary to ensure healthy plant growth. Additionally, inspecting the bed for signs of rot or damage and replacing worn-out components, such as deteriorating wood or rusted metal, can help prolong its lifespan.
Can garden beds be placed on uneven ground or slopes?
Yes, garden beds can be placed on uneven ground or slopes with proper preparation. It's essential to level the area as much as possible and consider using retaining walls or terracing techniques to prevent soil erosion and ensure stability. Additionally, adjustable legs or shims can be used to level the garden bed on uneven surfaces.